When to buy when to sell: Overvalued vs Undervalued market.
How to analyse company's valuation with PB and PE ratio.
Recently I learned about overvalued and undervalued markets and riding on it, did some deep-dive research to get it to play the game and win it. Let’s start with basic concepts:
What is Face Value?
What are Book Value and Market Value?
How to calculate the PB ratio?
How to analyze the valuation of the company?
What is the PE ratio?
How to calculate the PE ratio?
What is good PE and PB ratio?
What is Face Value?
When a company registers itself as a Private limited company, the owners of the company has to assign directors and invest some capital in the company. The capital is called equity capital, which is being invested by promotors or investors.
And shares are issued with total equity capital, and those issued shares have values known as Face Value.
The original value of a share in the share certificate is called "Face Value".
Equity Capital = Face Value X Numbers of sharesLet's assume that Company A, has 1 Crore total equity capital, the company choose to issue 10 lakh share only, then the face value of each share will be 10 Rs.
Equity Capital = 10 Rs. X 10 Lakh
Equity Capital = 1 cr.
Equity Capital = Legal capital that must be maintained in the business. It is a kind of reserved. Funds over and above the equity capital can be distributed to investors as dividends.
The face value doesn't change with time unless stock is split.
For example, Company A has decided to increase its shares so it must split it.
If the existing shares are 10 Lakh and the company wants to increase them to 20 Lakhs then the face value will be halved.
Equity Capital = Face Value X No. of shares
1 Cr. = 10 rs X 10 Lakh shares
1 Cr. = 5 rs X 20 Lakh Shares.
What is Book Value
The accounting value of shareholder's equity. Value of total assets in the accounting book.
Book Value is equal to the net assets of the company. This is the amount the shareholders will get if the company goes bankrupt.
Book Value Formula = (Total Assets – Liabilities – Intangible Assets) / Number of outstanding sharesAlso known as the Net Worth of the company, or shareholders equity.
What is the PB ratio?
Price to Book Value is a type of valuation ratio that calculates a stock’s intrinsic value. It helps you understand if a stock is undervalued, overvalued, or fairly priced.
There are two formulas to calculate the price to book value. Both formulas provide the same answer.
Price to Book Value = Market Capitalisation / Book Value of Assets
Price to Book Value = Current Market Price / Book Value per Share
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets like patents, intellectual property, goodwill, etc are not included while calculating a company’s book value. Only appreciating hard assets like cash, land, gold, plant, machinery, etc. are considered.
Tangible Assets
Fixed assets, also known as long-lived assets, tangible assets or property, plant, and equipment, is a term used in accounting for assets and property that cannot easily be converted into cash.
Outstanding Shares
Outstanding shares are the total number of shares available in the secondary market. Through outstanding shares, investors can measure a stock’s liquidity.
Outstanding shares is calculated by adding all the shares held by:
Retail investors (floating stock)
Company employees (as part of employee stock option plan)
Institutional investors like banks, pension funds, etc
How to calculate Book Value per share and PB ratio?
For example, Company A has total assets of 20 Cr, and 15 Cr. as the Equity Capital and 5 Cr loan. as Liabilities and has, a total of 10 Lakhs share issued.
Book Value = Tangible Assets - Liabilities
Book Value = 20 Cr. - 5 Cr. = 15 Cr.
Book Value Per Share = (Total Assets - Liabilities ) / No. of outstanding shares = ( 20 Cr. - 5 Cr.) / 10 Lacs shares
= 150 Rs.
Book Value of 1 Share = 150 rs.
Price to Book Value = Share Price / Book Value Per Share = 200 Rs. / 150 Rs. = 1.33 Rs
That means people are ready to pay 50 rs. per share
This means that investors are paying 1.33 rupees for one rupee of the company's assets.
Price to Book Value = Market Value(Market Cap) / Book Value
= 20 cr. / 15 Cr.
= 1.33 cr.
That means people are ready to pay 5 cr. worth of premium
Market Cap = Share Price X No. of shares
= 200 Rs X 10 Lakh
= 20 Cr.
Example Reliance Industries.
Let us calculate the price to book value (PB) ratio for Reliance Industries Ltd.
Current Share Price = Rs 1,959
Total Assets = Rs 13,21,212 (crores)
Total Liabilities = Rs 6,21,040 (crores)
Outstanding Shares = 634 (crores)
Step 1: Calculate book value per share.
Book Value per Share Formula = Total Assets – Liabilities / No of Outstanding Shares
= (Rs 13,21,212 – Rs 6,21,040) / 634
= Rs 1,104
What does a book value of Rs 1,104 mean?
It means that investors will get Rs 1,104 after paying Rs 1,959 (as share price) in case Reliance Industries goes bankrupt.
Step 2: Price to Book value is calculated by dividing a stock’s current market price by book value per share.
Price to Book Ratio = Current market price/book value per share
= Rs 1,959 / Rs 1,104
= 1.77
Book value is the value of assets, that is 15 Cr. but the market is ready to sell it for 20 cr.
Why the market is ready to pay a premium on book value?
Perception about the future growth of the company.
Value of intangible assets (brand, technology, copyright) employees, leadership strategy, etc.
When is the PB ratio useful?
Asset heavy industries - for example, Oil, Gas, manufacturing, Infrastructure, Real state, etc.. These sectors generally have a low PB ratio, because of large tangible assets
When is the PB ratio not useful?
For technology and services industries, software, consultancy, etc. generally have low PB ratio as they have more intangible assets than tangible assets.
What is the Ideal Price to Book Value?
Like most financial ratios, even the PB ratio differs across industries. But the ideal price to book value is less than or equal to 1. This signals an undervalued company. However, price to book value up to 3 is also acceptable. High price to book value companies are overvalued and do not fit the value investing criteria.
Price to book value can also be negative. The main cause behind a negative PB ratio is consistently negative cash flow. Another reason is when total loss wipes off shareholders’ equity capital.
How to use the PB ratio to discover an overvalued stock?
Overvalued stocks will generally have a combination of low return on equity and a high price to book ratio.
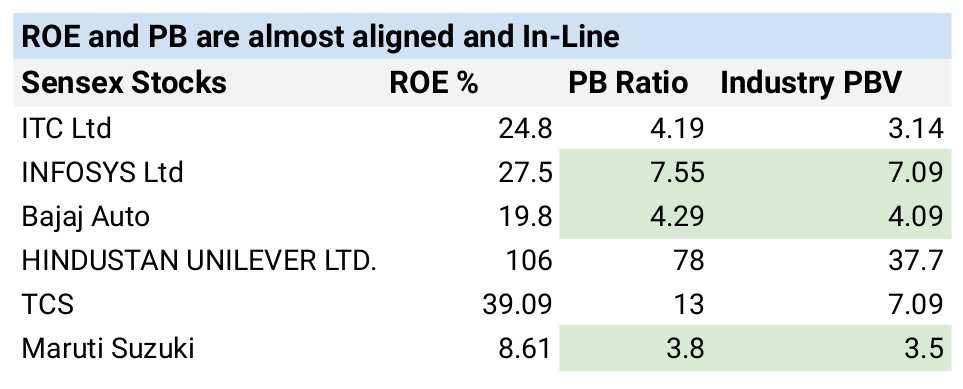
ROE and PB ratio relation.
ROE measures a company’s ability to generate a return on its assets. Ideally, ROE should be in line with the price to book value. An abnormal deviation can be a potential red flag for investors.
Avoid PB ratio
Buy PB ratio
below is the industry price to book value of top sectors as of October 2021
Undervalued stocks are expected to go higher; overvalued stocks are expected to go lower, so these models analyze many variables attempting to get that prediction right. However, the data point that all the models have in common is a stock's price-to-earnings ratio.
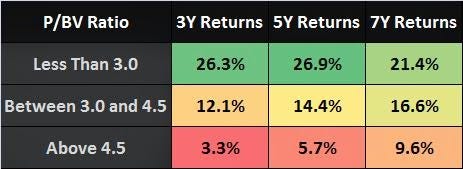
The table above clearly shows that if one is investing in markets where P/BV < 3.0, returns over the next 3, 5, and 7 year periods have been in excess of 20% that is 26.3%, 26.9%, and 21.4% to be precise. On the other hand, if the investment is made when index P/BV exceeds 4.5, the returns have been quite unacceptable at 3.3% and 5.7% for 3 and 5 year periods
For your information, currently Nifty is trading at a P/B Ratio of 3.4
But here is another interesting thing which can be observed. Even at a costly PB>4.5, if an investor stays invested for more than 7 years, then average returns are still a very decent 9.6%. And this shows that the longer you stay invested, the higher are the chances of making money in the stock market.
PE Ratio
In general, a high P/E suggests that investors are expecting higher earnings growth in the future compared to companies with a lower P/E. A low P/E can indicate either that a company may currently be undervalued or that the company is doing exceptionally well relative to its past trends.
P/E = Price Per share / Earnings Per Share = 150 / 50 = 15
That means that whatever the company earns annually, people are ready to give 15 times its earnings.
Low PE :
Stock is undervalued
Low growth or negative growth
Future prospects not good
High PE:
Stock is overvalued
High Growth
Great future prospects
How to check PE the right way.
P/E ratio to be compared with peer or industry average
Why PE is high or low?
Growth is sustainable or temporary?
Low PE and Low or Negative Growth Avoid these kinds of stocks.
High and Moderate PE with High Growth
For a more detailed analysis of data from 1999 to 2019 visit - https://stableinvestor.com/2019/01/nifty-pe-ratio-returns-analysis-updated.html
Sources:
https://stableinvestor.com/2015/03/pb-ratio-analysis-india-2015.html
https://stableinvestor.com/2019/01/nifty-pe-ratio-returns-analysis-updated.html











great work
great blog!